What is D-Sub input?
Communication between devices is the basis of automation. Although wireless connections are constantly improving, they are susceptible to interference and are characterized by a certain delay in signal transmission, so they are used mainly in smart home systems and much less often in industry.
Communication expectations between industrial devices have changed over the years and new technologies have emerged with them. Nowadays it is common to use Ethernet cables for communication between individual network elements. They allow very fast data transfer and can therefore transmit complex instructions between computers or controllers and executive devices or operator panels. However, until some time ago, connections in the industry were based on D-Sub connectors.
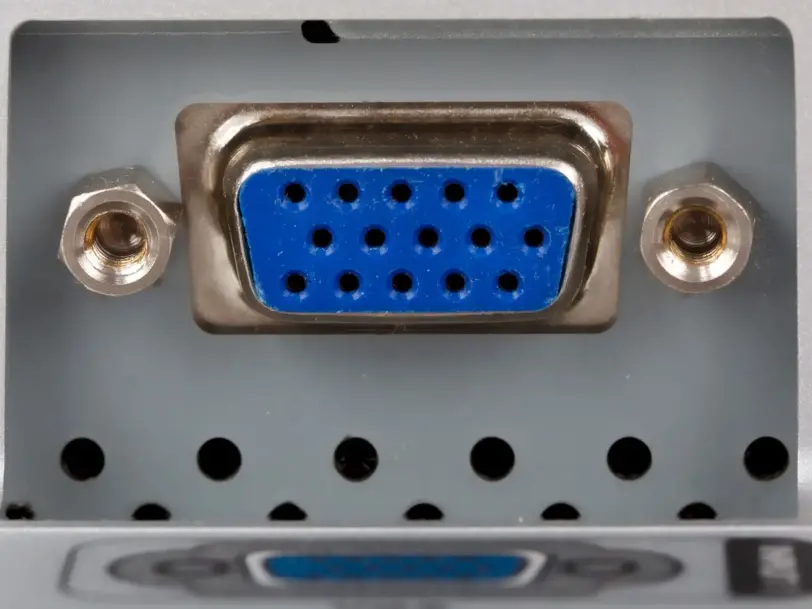
What is D-Sub?
D-Sub is a family of connectors used for communication between electronic devices. The letter “D” in its name comes from the characteristic shape of the plug or socket resembling this letter. There are many types of D-Sub sockets. The smallest ones in the standard version have 9 pins and the largest ones have 104 pins.
D-Sub connectors date back to the 1950s, but they are widely used today. One reason is that many places still use devices made in the last century, when they were most common. The most popular application of D-Sub connectors is communication via RS-232 and RS-485 interfaces. It allows you to establish more or less extensive connection networks between devices used in industrial warehouses.
The first of these interfaces, RS-232, was used in the past mainly to connect end devices and various peripheral devices such as a printer or keyboard to the computer. It was also used to connect the computer to the modem. In daily use, they have been replaced by USB and Ethernet connectors, which are now used on a large scale.
D-Sub interfaces RS-232 and RS-485
However, RS-232 is still used in industry. In some businesses it is still used for communication between the computer and PLC modules or HMI panels. However, there is a downside. The use of the RS interface is possible with a maximum length of 15 meters and a speed of 20 Kbit/s. On longer cables, voltage drops may be too large to effectively transmit the signal to the connected device. Initially, RS-232 was used to use the Modbus protocol, but over time this function was taken over by RS-485.
RS-485 is in a way an extension of the RS-232 interface. It allows data transfer in the form of a bus between various devices. It is faster than the aforementioned interface and more resistant to interference. RS-485 can operate at 35 Mbit/s for a length of up to 10 meters, but the length of a single cable can be up to 1200 meters depending on the need. Additionally, 32 devices can be connected using the RS-485 protocol.
The repeater allows you to connect additional devices operating on one line or increase the distance that can split individual devices by another 1200 meters. Unlike RS-232, 485 uses a differential voltage, allowing it to operate over longer distances than the simpler 232 interface.
D-Sub usage areas
Companies still use D-Sub connectors because in most cases networking based on RS-232 or RS-485 protocols still works. In addition to Modbus RTU networks, RS-232 and RS-485 connectors, that is, D-Sub connectors, are also used in Profibus DP networks.
D-Sub connectors are sometimes used for control when complex commands do not need to be transmitted. A characteristic element of the D-Sub connector are the screws on both sides of the plug. They help secure the plug properly in the outlet, but also protect against accidentally unplugging it. This is one of the reasons why D-Sub connectors are still common in the rail industry.
Securing the connection with bolts reduces the risk of the cable becoming loose due to the effect of vibration on the connection. When we talk about a moving train, it is undeniable that the vibrations are not small and can actually affect the loosening of the spark plugs in extreme cases.
The most popular but outdated implementation of D-Sub connectors is the classic VGA connector used to connect monitors. Initially, this standard was replaced by the DVI connector, but over time, the most popular connector through which monitors were connected to the computer became HDMI.