What is a good thermal conductivity for thermal paste?
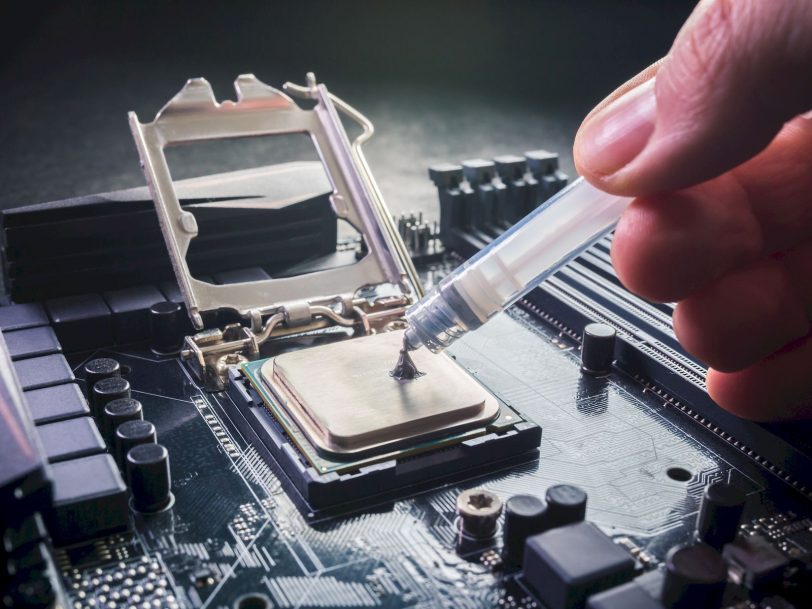
Thermal paste is a must-have item for those who want to build a PC or need to upgrade their PC. It is also essential to replace the said thermal paste after using it for a few years, because it is not permanent and degrades over time, reducing the efficiency of the heatsinks, especially in the CPU and GPU, causing the chips to heat up more. Despite all this, its properties such as thermal conductivity are still largely unknown by many.
What is thermal conductivity?
Thermal conductivity (often denoted by k, λ, or κ) refers to the intrinsic ability of a material to transfer or conduct heat. It is one of the three methods that objects have to transfer heat, the other two being convection and radiation. In the case of conduction, the transfer of heat from one body to another takes place by contact, through materials. The rate of heat transfer is based on Fourier’s law. In this case, it is about how easy it is for the thermal paste to absorb heat from the chip and transmit it to the heatsink of the cooling system.
Regarding the way in which the thermal conductivity of one material to another is produced, it is done through agitation and molecular contact, and does not give rise to the volume movement of the solid itself. Heat moves along a temperature gradient from an area of high temperature and high molecular energy to an area of lower temperature and lower molecular energy. This transfer will continue until thermal equilibrium is reached between both zones, that is, when both are at the same temperature, therefore there is no longer a transfer from one to the other. The rate at which heat is transferred depends on the magnitude of the temperature gradient and the specific thermal characteristics of the material.
Obviously, in a cooling system, what is always intended is that this equilibrium is never reached, so that it is always transferring heat and cooling the chip. In these cases it is achieved by means of heatsinks, fans, or liquid cooling that help to reduce the temperature of the other side so that it is always lower than that of the heat source, in this case the chip.
Thermal conductivity is quantified using the International System of Units (SI) unit of W/m-K (watts per meter per degree Kelvin), and is the inverse of thermal resistivity, which measures an object’s ability to resist the transfer of heat. heat.
The thermal conductivity of a thermal paste is highly dependent on a number of factors. Among them, the temperature gradient, the properties of the material that said paste is made of, and the length of the path followed by the heat (in this case, the thickness).
On the other hand, it is important to know that since molecular motion is the basis of thermal conductance, the temperature of a material has a great influence on thermal conductivity. Molecules move faster at higher temperatures, and therefore heat is transferred through the material at a higher rate. This means that the thermal conductivity of the same sample has the potential to change dramatically as the temperature increases or decreases. Another important factor regarding the choice of the type of base material of the thermal paste.
The ability to understand the effect that temperature has on thermal conduction is critical to ensuring that products behave as expected when subjected to thermal stress, such as in electronics.
How does the conductivity of thermal paste affect its efficiency?
In short, taking this into account, the greater or better the thermal conductivity of a thermal paste, the better it will perform its function. Therefore, when buying a new thermal paste, take a good look at the conductivity values provided by the manufacturer, since you will see that some are superior to others…